When moving to or living in Mexico, understanding the healthcare system is essential for ensuring your well-being. Mexico offers high-quality healthcare options that are often significantly more affordable than in the U.S. or Canada, making it an attractive destination for lots of people. However, navigating the system requires knowledge of its unique structure and practices. This article provides an overview of 5 of the most important aspects of healthcare in Mexico that foreigners need to know.
1) Mexico’s Healthcare System is Dual-Tiered: Public and Private Options
Mexico’s healthcare system is divided into two main sectors: public and private healthcare. Each provides different levels of service, access, and costs. Understanding these options is key to making an informed decision about your healthcare needs in Mexico.
Public Healthcare
Mexico’s public healthcare system is extensive, and foreigners with temporary or permanent residence status can also benefit from these services. Mexico offers a number of public healthcare programs, including Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS), IMSS-Bienestar, Instituto de Seguridad y Servicios Sociales de los Trabajadores del Estado (ISSSTE), and Instituto de Seguridad Social para las Fuerzas Armadas Mexicanas (ISSFAM). However, for the overwhelming majority of foreigners with residency, only IMSS and IMSS-Bienestar are applicable. IMSS is Mexico’s primary social security healthcare system and is available to residents who enroll voluntarily. IMSS-Bienestar provides basic healthcare services to those without access to IMSS or private insurance. Meanwhile, ISSSTE is specifically for government employees and retirees, and ISSFAM is reserved for members of the military and their families.
Please note that due to recent legislation, some of the information below is in the process of being updated and may not be yet reflected on the IMSS’ website. For example, based on anecdotal reports, it appears that there will be a single set annual fee for foreigners with residency, irrespective of age. Additionally, having a pre-existing condition may no longer preclude you from enrolling and receiving coverage.
IMSS: This is the largest public health insurance program in Mexico, funded through payroll taxes and individuals (e.g., legal residents) who voluntarily opt-in. It primarily serves employees, retirees, and their families. For foreigners who are not employed in Mexico, there is the option to enroll voluntarily for an annual fee. The enrollment process is relatively straightforward if you speak Spanish and can be done at your local IMSS facility. If you are not fluent in Spanish, it is probably advisable to hire a facilitator who can help guide you through the process.
However, it’s important to note that some pre-existing conditions are either excluded all together or not immediately covered. Some enrollees must wait up to 2 years before their conditions are included under their IMSS’ policy. Furthermore, while IMSS hospitals in larger cities are generally well-equipped, smaller rural clinics may have limited resources and long wait times. However, the opposite may also hold true in some instances, where you may find newer facilities in smaller towns. IMSS is probably the most affordable healthcare option, but it comes with a trade-off in terms of service levels.
IMSS-Bienestar: This is a public healthcare program primarily designed to serve individuals who do not qualify for IMSS or private insurance, including many lower-income families and those in rural or underserved areas. It provides free or low-cost healthcare services, with a focus on primary and preventive care. The program operates hospitals and clinics across the country, often in regions where other healthcare options are limited.
While IMSS-Bienestar aims to ensure access to basic medical care, the quality of services can vary significantly depending on location. Facilities in urban areas may offer more comprehensive care, while rural locations often face challenges such as shortages of medical personnel and equipment. Similar to IMSS, patients may experience long wait times for appointments and treatments.
IMSS-Bienestar is particularly beneficial for those who prioritize affordability and access to general health services, but it may not be the best option for individuals with complex or specialized medical needs who require quick and efficient care.
Challenges of Public Healthcare: While the public system offers affordable care, there are several drawbacks, especially for foreigners who may be used to more immediate and specialized services. Wait times in public hospitals and clinics can be long, especially for non-urgent procedures. Additionally, some public hospitals, especially in rural areas, may lack the advanced technology and medical equipment seen in private hospitals.
Furthermore, public healthcare services in Mexico, particularly those under IMSS and INSABI, often have language barriers. While larger cities and areas with foreigners may have English-speaking doctors, this is not always the case in more remote regions. As such, foreigners should consider taking Spanish lessons or using translation apps when accessing public healthcare.
Private Healthcare
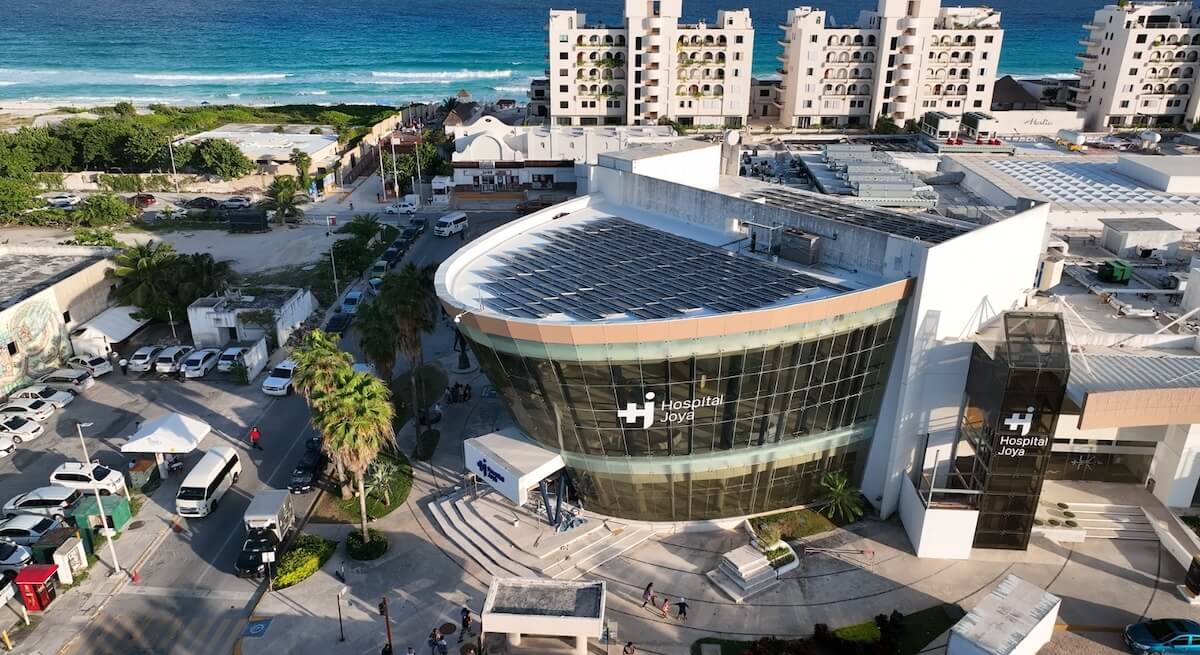
The private healthcare sector in Mexico is often seen as the most reliable and efficient choice for foreigners. It is generally well-regarded for its advanced technology, short wait times, and access to highly qualified medical professionals who may have trained internationally.
Benefits: One of the main advantages of private healthcare in Mexico is the high quality of care provided. Private hospitals are often comparable to those in the U.S. and Europe, with state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment, modern facilities, and access to highly trained specialists. Many private hospitals employ staff who speak English, which can ease communication issues for non-Spanish speakers.
The cost of private healthcare in Mexico is also significantly lower than in the U.S. or Canada. For example, a routine consultation with a general practitioner in a private clinic may cost between $500 – $1,000 MXN and hospital stays and surgeries can be upwards of 40 – 60% less expensive, in some instances, than in the U.S.
Private Health Insurance: Private coverage is widely available in Mexico, and it covers a broad range of services, including hospital visits, surgery, specialist consultations, and even dental care. However, the cost of private insurance can vary significantly based on factors like age, medical history, and coverage level. Some plans also have exclusions and waiting periods for pre-existing conditions, similar to IMSS.
Many foreigners opt for international health insurance plans that offer coverage both in Mexico and abroad. Companies like Cigna, Allianz, and GeoBlue provide comprehensive global coverage for foreigners. These plans may be more expensive than local Mexican plans but offer flexibility and the option to receive care in multiple countries.
2) Health Insurance Options for Foreigners in Mexico
When relocating to Mexico, understanding the available health insurance options is one of the most critical decisions you’ll make regarding your healthcare needs. While the public system may be appealing due to its affordability, many foreigners choose private health insurance to ensure a higher level of care.
There are 3 main types of health insurance available to foreigners in Mexico: local private insurance, international insurance, and travel insurance. Each type of insurance offers different levels of coverage and is suitable for different situations.
Local Insurance: Local private health insurance policies are more affordable than international plans and are often sufficient for residents who plan to stay in Mexico for extended periods. These plans cover a range of medical expenses, including doctor’s visits, emergency care, hospital stays, and surgeries. Most local health insurers also offer additional coverage for dental and vision care.
International Insurance: International health insurance provides global coverage, which is ideal for foreigners who travel frequently or plan to spend time in multiple countries. These plans are often more expensive than local insurance policies but are useful for those who want coverage wherever they go. International health insurance plans from companies like Cigna, Allianz, and GeoBlue offer flexible coverage, including access to some of the best healthcare providers in Mexico and abroad.
Travel Insurance: Travel insurance is typically purchased by short-term visitors to cover emergency medical expenses during their stay in Mexico. While this type of insurance can be more affordable than other plans, it generally does not provide coverage for long-term medical conditions or non-emergency treatments. For long-term residents, travel insurance is usually not adequate, and a more comprehensive insurance plan is necessary.
Practical Tip: When choosing a health insurance plan, ensure that it covers medical evacuation, especially if you live in a rural area where access to advanced care may be limited. Evacuation insurance covers the cost of transporting you to the nearest major hospital in the event of a medical emergency.
3) Prescription Medications: Affordable and Accessible
One of the most notable benefits of healthcare in Mexico is the accessibility and affordability of prescription medications. Many medications that are available by prescription in the U.S. or Canada can be bought over-the-counter (OTC) in Mexico. Prices for medications are also significantly lower than in the U.S. or Canada, which makes ongoing treatment more affordable for people with chronic conditions.
Types of Pharmacies:
-
- Chain pharmacies: Large pharmacy chains like Farmacias Guadalajara, Farmacias del Ahorro, and Farmacias Benavides are ubiquitous in Mexico, offering a wide range of medications at affordable prices. These pharmacies typically offer over-the-counter medications, and you can find both brand-name and generic options.
- Independent pharmacies: Smaller, independent pharmacies are also common in local neighborhoods. They may offer competitive prices but sometimes carry fewer options. It’s advisable to be cautious and ensure that the pharmacy is well-known and reputable to avoid counterfeit medications.
- Hospital pharmacies: Larger hospitals, especially private ones, often have in-house pharmacies where you can purchase both prescription and over-the-counter medications. These pharmacies tend to carry more specialized treatments that may not be readily available at retail pharmacies. The prices also tend to be higher.
Prescription Medication Process: In Mexico, medications are often more affordable than in the U.S. and Canada, and the process for obtaining medications is relatively simple. Many medications can be purchased without a prescription. However, certain medications, such as antibiotics, narcotics and more potent drugs, still require a prescription from a licensed doctor.
Practical Tip: Always check the generic name of your prescribed medication before traveling to Mexico, as the brand name may differ. A list of your medications, including both generic and brand names, can help ensure a smooth transition when refilling prescriptions.
For a more in-depth discussion of pharmacies, be sure to read the Pharmacies in Mexico article.
4) Quality of Healthcare Varies by Region
Mexico has made tremendous progress over the years in its healthcare system, but the quality of care can still vary significantly depending on the region. Major urban centers typically have the best access to high-quality healthcare, but rural and remote areas may not have the same level of medical resources.
Urban Areas: Cities like Mexico City, Guadalajara and Monterrey, are home to top-tier healthcare facilities and medical professionals who have trained internationally. Foreigners living in these areas will find that hospitals and clinics provide modern treatments and cutting-edge technology, often on par with what you would expect in the U.S. or Canada.
Rural Areas: In contrast, healthcare in rural or more remote parts of Mexico can be limited. Many small towns only have basic clinics staffed by general practitioners, and specialty care or advanced treatments may require traveling to the nearest city. Healthcare professionals in rural areas may also face limited resources and lack access to the latest medical technology.
Practical Tip: If you plan to live in a remote area, private health insurance with coverage for medical evacuation is highly recommended. This ensures that you have access to the best care when needed, even if it means being transported to an urban center for treatment.
5) Cultural Differences and Practical Tips
Navigating healthcare in a new country requires an understanding of cultural differences and local practices. Mexico’s healthcare system has a different approach to doctor-patient interactions, and understanding these differences will help you make the most of your medical experiences in the country.
Doctor-Patient Interactions: In Mexico, healthcare providers generally prioritize a more personalized approach to patient care. Unlike the often brief consultations typical in the U.S. or Canada, Mexican doctors tend to spend more time with patients to understand their medical history and current concerns. This can be a significant advantage for foreigners who need a more holistic view of their health.
Language Barriers: In major cities and tourist areas, English-speaking doctors are widely available. However, outside of these areas, language can be a barrier. Many healthcare professionals in rural areas may only speak Spanish, so it’s important to learn basic medical Spanish or use a translation app to ensure clear communication during medical consultations.
Additional Considerations for Foreigners
Mexico is a popular destination for retirees and long-term residents, and the country’s healthcare system is well-suited to meet their needs. In addition to basic medical services, Mexico also offers a range of healthcare options that cater to foreigners looking for specialized care, medical tourism, and preventive services.
Medical Tourism: Mexico has become one of the leading destinations for medical tourism, offering affordable treatments like dental work, cosmetic surgery, bariatric surgery, and fertility treatments. The quality of care in these areas is often comparable to what you would find in the U.S., but at a fraction of the price. Many private hospitals in Mexico offer comprehensive services for medical tourists, including language assistance and concierge services.
Specialist and Chronic Care: Foreigners with chronic conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or cancer can find affordable, high-quality care in Mexico. Specialist care is readily available in urban centers, and many doctors are trained abroad and speak English.
Helpful Online Resources
Stay up-to-date on all relevant information in relation to IMSS, INSABI, and general healthcare information, as outlined in this article, by checking the following websites:
-
- Gob.mx: Mexico’s official federal government portal with details on all government matters, including providing detailed information on healthcare services.
- IMSS: Learn about IMSS enrollment, coverage and healthcare facilities.
- IMSS-Bienestar: Information about public healthcare services for those without IMSS.
- Asociación Mexicana de Instituciones de Seguros (AMIS): Information on private health insurance options in Mexico.
Conclusion
Healthcare in Mexico offers a unique combination of affordability, accessibility, and quality. Whether you choose public or private care, you’ll have access to a range of options to suit your medical needs. By understanding the two-tiered system, exploring your insurance options, and familiarizing yourself with the local healthcare landscape, you can make informed decisions about your care.
Living in Mexico comes with many benefits, and having access to affordable, quality healthcare is one of the key reasons many foreigners choose to call this country home. With proper planning, you can enjoy excellent medical services and live with peace of mind, knowing that your healthcare needs will be well taken care of.
This article provides general information about healthcare in Mexico and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with qualified healthcare professionals regarding your specific medical needs.
Please feel free to leave us a comment below about your personal experience with accessing and receiving healthcare in Mexico. We would love to hear from you! Additionally, if you found this article helpful, consider sharing it with others who might benefit from it. A quick share goes a long way in helping others discover useful information!









Excellent article. Thank you.
Thank you very much for the kind words and you’re welcome!